Who are Healthcare workers?
A Health Care Worker (HCW) or Health Care Professional (HCP) is one who provides health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. They include Doctors, Nurses, Physiotherapists and Pharmacists who perform services related to Health Care.
Why is Hand Hygiene critical for HCWs?
Hand Hygiene is especially important for HCWs because poor hand hygiene by HCW can lead to
Health Care Associated Infection (HCAI), which is a major cause of death and disability worldwide. HCAI, otherwise known as Nosocomial infection, is an infection acquired by a patient or their caretaker from a hospital or healthcare facility.
HCAI can lead to
- Prolonged hospital stay
- Long term disability
- Increased resistance of microorganisms to antimicrobials
- Additional financial burdens
- More deaths
- High costs for the health systems
- Emotional stress for patients and their families
Prevalence of HCAI
Prevalence of HCAI | |
In Developed Countries | In Developing Countries |
USA - 4.5% | BRAZIL - 14.1% |
U.K & IRELAND - 7.6% | MALAYSIYA - 13.9% |
FRANCE - 6.7% | THAILAND - 7.9% |
ITALY - 4.6% | MOROCCO - 17.8% |
SWITZERLAND -10.1% | TANZANIA - 17.8% |
As per studies HCAI affects 5–15% of hospitalized patients and 9–37% patients admitted in ICUs.
Causes for HCAI
Transmission of HCAI takes place through direct and indirect contact, droplets, air and any common medium. However, the most common method of transmission of HCAI is by way of the hands of HCWs, through the below process:
- Organisms which are present on one patient’s skin or surroundings, can be transferred to the hands of HCWs thus contaminating their hand
- Many of these organisms are capable of surviving for several minutes on HCWs’ hands
- When the HCW touches other patients or even objects that can be touched by others (such as door handles) with contaminated hands, the germ can pass on to others.
Hand Hygiene for HCWs
Practicing hand hygiene is thus a simple yet effective way to prevent HCAI. Hand Hygiene means cleaning hands by using soap and water or antiseptic hand rub (i.e. alcohol-based hand sanitizer including foam or gel). Cleaning hands with appropriate antiseptic agent can prevent the spread of germs, including those that are resistant to antibiotics. This can drastically reduce the risk of HCAI.
Two Methods for Hand Hygiene
- Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer
- Washing with Soap and Water
Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer
Alcohol-based hand sanitizers are the most effective in reducing the number of germs on the hands of healthcare providers and are preferred in most clinical situations.
When to Use an Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer
- Immediately before touching a patient
- Before placing or handling invasive medical devices, e.g. urinary catheters
- Before moving from work on a soiled body site to a clean body site on the same patient
- After touching a patient
- After contact with blood, body fluids or contaminated surfaces
- Immediately after glove removal
Washing with Soap and Water
Wash your hands with soap and water during Routine Patient Care, whenever they are visibly dirty, before eating, and after using the restroom.
When to Wash with Soap and Water
- When hands are visibly soiled
- After caring for a person with known or suspected infectious diarrhea
- After known or suspected exposure to spores
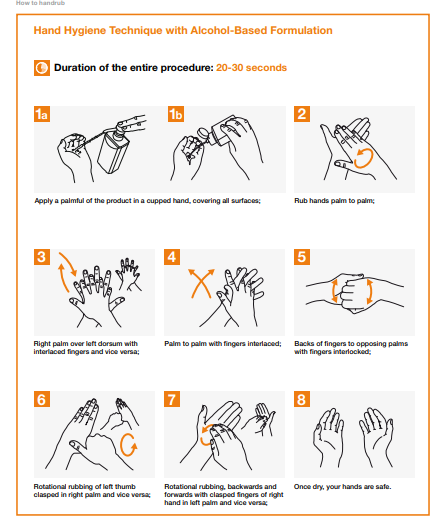
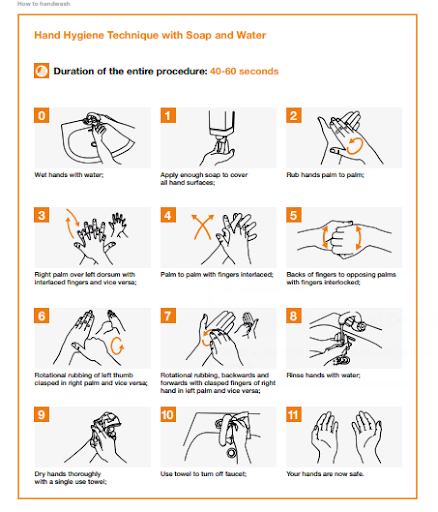
Hand hygiene is the most effective measure for reducing the transmission of microorganisms and HCAI both in the society and in the healthcare setting. As the techniques involved in hand hygiene are simple, it is feasible to ensure a high degree of compliance.

